Lambda
AWS Lambda 無伺服器運算服務筆記。
Features
- Serverless: Run code without provisioning or maintaining a server
- Automatic Scaling: Scale applications automatically as per the workload
- Pay per use: Billed per millisecond of use
- Performance consistency: Achieved by selecting the right memory size
- Language support: Multiple programming languages supported
Event Sources
Lambda starts with an Event.
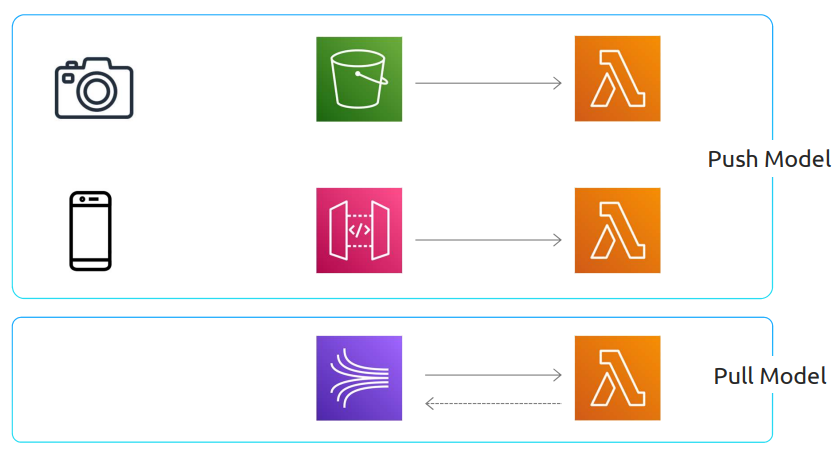
Push Model Source Types
Other service directly triggers Lambda when something happens.
Synchronous
Lambda returns a response back to the event source.

Asynchronous
Lambda places the event into a queue and immediately sends a success response back.
- If there’s an error during asynchronous invocation, Lambda will attempt to run the code three times in total
- Between each attempt, wait one minute
- If still fails, configure Lambda to send to a dead letter queue
- Configure Lambda Destination to send result to SNS, CloudWatch, etc.

Pull Model Source Types
Lambda periodically polls information flowing through a stream or queue.
- Stream: Lambda stops polling while retrying the message
- Queue: Lambda returns message to queue if invocation fails, keeps retrying until successful or expires

Access Permissions
Security is crucial because Lambda can run code and affect other AWS services.
Invocation Permissions
Only needed for push event sources. Granted through an IAM resource policy automatically created when configuring an AWS service as an event source.
Execution Roles
Grant Lambda permissions to interact with other AWS services.
Need 2 IAM Resource Policies:
IAM Policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Sid": "",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:PutObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::lambda_bucket/*",
"Condition": {
"ArnEquals": {
"lambda:SourceFunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:source_lambda"
}
}
}]
}Trust Policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}]
}Functions
Handler has two objects:
- Event Object: Allows event source to pass information to Lambda function
- Context Object: Generated by AWS, contains runtime environment information
Pricing
Total Cost = (Memory Allocated in GB) × (Duration in ms) × (Number of Requests)
- Memory: 128MB ~ 10GB
- Additional costs: ephemeral storage, Provisioned Concurrency
- CPU: Amount of memory determines CPU power allocated
Configuration
Ways to configure:
- AWS Management Console
- AWS CLI
- AWS SDKs
- AWS CloudFormation
Handler Format
<package_name>.<class_name>::<function>SnapStart
- Running code in the init phase
- No additional cost
- Configuration: Configuration TAB → General configuration → Edit → SnapStart → PublishedVersions
Use Cases
API Gateway Integration

Serverless Cron Job
定時任務

Event Processing (SNS & SQS)
Pub-sub pattern service

File Upload Processing with S3

Step Function Workflow
